On the Internet you can find dozens of different diets and lists of products that supposedly can “clean” blood vessels. We checked whether their effectiveness is supported by scientific evidence.
Publications about the benefits of proper nutrition for blood vessels and the fact that in this way one can “clean” blood vessels are found not only in blogs And Media, but also on websites district And urban hospitals. IN a number of publications are described traditional cleaning methods, manufacturers of dietary supplements advise clean blood vessels with garlic and lemon, in “biohacking clinics” are offered also droppers. Popular recipes for cleaning vessels with ethyl alcohol alcohol or peroxide hydrogen. More carefully about the importance of diet for atherosclerosis write on the Roskachestvo website, and the website of the Pirogov clinic reportsthat “cleaning blood vessels” is, in principle, not a medical term.
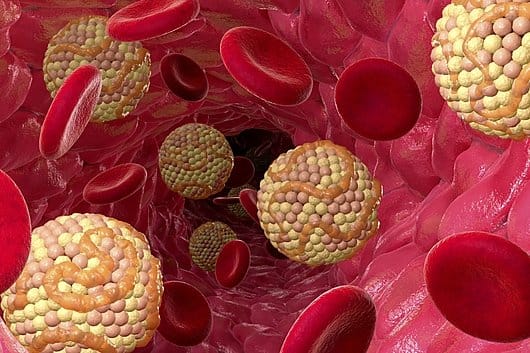
Cholesterol plaques form and clog blood vessels in pathologies such as atherosclerosis - a chronic inflammatory disease arteries. Lipids (mainly cholesterol), as well as other substances accumulate near the walls and create dense plaques that narrow the lumen of blood vessels and disrupt blood flow. Atherosclerosis is main cause of cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial infarctions, strokes and peripheral vascular pathologies.
Cholesterol plaques consist from several components. The bulk is fibrous tissue, including collagen and other extracellular matrix proteins that form the plaque capsule and give it structural strength. Inside the plaque there is a fatty core saturated with lipids: crystalline cholesterol, cholesteryl esters and phospholipids. In addition, the structure of plaques contains smooth muscle cells, macrophages and T-lymphocytes - immune cells involved in the inflammatory process. Over time, inside the plaque may happen calcification, which adds hardness to the membrane and reduces the elasticity of the vascular wall.
Formation of atherosclerotic plaques begins with dysfunction of the endothelium - the inner layer of the artery: low-density lipoproteins (LDL, or bad cholesterol) are retained and accumulate in the subendothelial space. Oxidized LDL causes activation of immune cells, which in turn take up lipids, creating inflammatory reaction. The subsequent production of dead cells and cellular debris leads to the formation of a necrotic plaque core. In this case, inflammation and the immune response contribute to the thinning of the fibrous capsule, and this increases the likelihood of plaque destruction and arterial thrombosis.
The danger of cholesterol plaques is that they narrow the lumen of blood vessels, reducing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to organs, causing tissues to suffer from ischemia. In addition, unstable and fragile plaques can rupture, leading to the formation of blood clots, a leading cause of acute heart and vascular disease (eg, myocardial infarction and stroke). Inflammation around plaques accelerates development of the disease and worsens the prognosis of the disease.
There can be many causes of atherosclerosis. TO classic Risk factors include age, gender (men susceptible disease at a younger age, and in women the risk increases after menopause), smoking, high cholesterol, especially low-density lipoprotein and low high-density lipoprotein, hypertension and diabetes.
In addition, in recent years, much attention is given new (or so-called auxiliary) risk factors. Among them are chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, disorders microbiota intestines, affecting metabolism and inflammatory responses, environmental and behavioral factors (air pollution, chronic stress, physical inactivity, poor diet and obesity). All these factors contribute to the development and progression of atherosclerosis.
An unhealthy diet does indeed increase the risk of developing pathology, but adding or removing certain foods from your diet unlikely will help remove formed plaques. As already noted, lipid deposits are located in a fairly dense capsule. To date, there is not a single drug that could effectively destroy this capsule and remove its contents from the bloodstream, note both Russian and foreign experts.
Clinical pharmacologist and teacher at Russian National Research Medical University named after. N. I. Pirogova Andrey Kondrakhin notes: “An atherosclerotic plaque is a serious pathological phenomenon, it consists of many elements... we simply do not have the ability to influence the plaque and destroy it by simply using various chemicals.” Croatian scientists in the article “Cleansing blood vessels” also indicate: “There are no safe or effective treatments to clear blood vessels of the lipid accumulation and calcium deposits involved in atherosclerosis.” Experts from the Harvard School of Public Health also reportthat it is impossible to dissolve cholesterol plaques, but they clarify: “Changing lifestyle and taking medications can stabilize already deposited accumulations and reduce them in size.” First of all, we are talking about taking statins - drugs that block the liver enzyme that promotes the production of cholesterol. Thus, a plaque blocking 30% of the lumen of blood vessels can be reduced by half.
In addition, if large plaques block the lumen of blood vessels, then Maybe Surgery such as balloon angioplasty may be required. During this operation, a catheter with a balloon at the end is inserted into the affected artery and the balloon is inflated and deflated several times. This allows you to “press” the plaque against the wall of the vessel and improve blood flow in it.
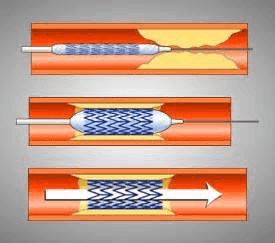
To prevent re-narrowing, a stent - a wire frame - may be installed in the artery. For maximum effect, the stent can be coated with slow-release drugs, primarily the already mentioned statins.
If the plaques are so large that angioplasty and stenting do not help, the patient undergoes bypass surgery - creating a new path for blood bypassing the blocked area of the artery affected by atherosclerosis. Finally, using endarterectomy the plaque can be detached from the artery wall mechanically, and the damaged area can be sutured. Also carry out atherectomy, in which plaques are destroyed using catheters equipped with cutting, drilling, grinding or crushing tips.
It turns out that modern medicine, in principle, has no way to dissolve cholesterol plaques due to their hard shell. Plaques can be removed only by acting on them mechanically - by cutting, crushing or peeling off from the wall. Neither nutrition nor medications, alas, can remove already formed plaques. Moreover, some recipes for “cleaning” blood vessels are simply unsafe - for example, beliefthat you can clear plaque from blood vessels by regularly drinking alcohol, since cholesterol dissolves in ethyl alcohol. No less dangerous A way to “clean” blood vessels is to use hydrogen peroxide internally (and even more so in the form of droppers).
However, diet is an important part of the treatment of atherosclerosis. By following a proper diet (Mediterranean or DASH diet to control hypertension), Can reduce the likelihood of new plaques appearing and old ones becoming larger. However, diet alone will not achieve the desired result. Specialists recommend maintain an optimal level of physical activity: weekly 150–300 min. medium-intensity loads and 75–150 high-intensity loads.
Thus, to date, not a single substance has been discovered that could effectively dissolve cholesterol deposits in blood vessels. Therefore, there is no magic recipe or set of products that can break down plaques and “clean” blood vessels. The only way to clean the vessels is to mechanically remove these deposits. At the same time, proper nutrition is beneficial for patients with atherosclerosis, as it prevents the appearance of new cholesterol plaques.
Cover image: TLECOATL ZYANYA, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
If you find a spelling or grammatical error, please let us know by highlighting the error text and clicking Ctrl+Enter.