On September 7, during a direct line with citizens, the governor of the Rostov region Vasily Golubev said that the antibiotic was first isolated by the Soviet microbiologist Zinaida Ermolyeva. We decided to check if this is true.
During the direct line, the Rostov governor stated: “Zinaida Vasilievna Ermolyeva... This is that woman... She is our countrywoman, who was called “Madame Penicillin.” She invented penicillin. Once upon a time the British argued that they were the first. No". Subsequently, the regional administration did not receive any refutations or clarifications of what Golubev said.
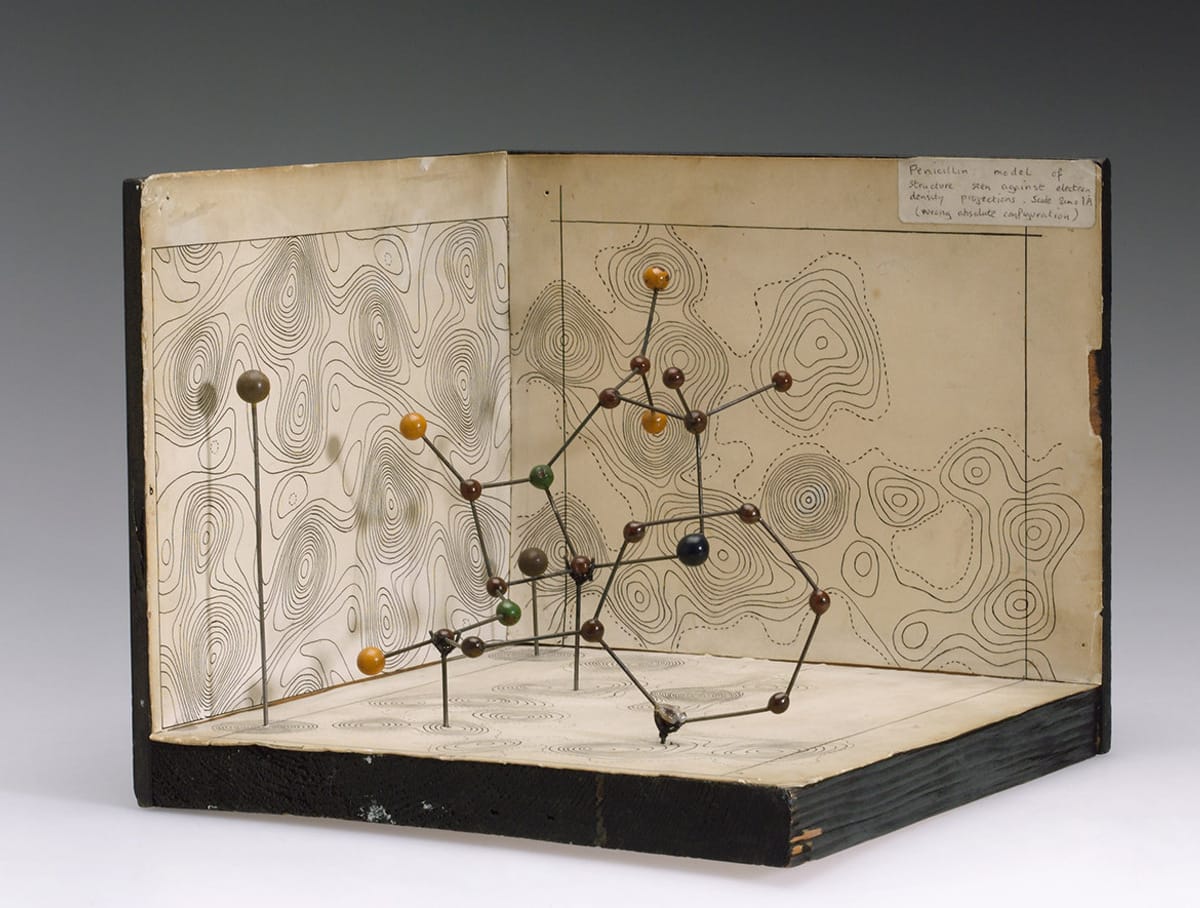
Penicillin is an antibiotic obtained from the mold Penicillium notatum. First scientific article, dedicated to this drug and its antibacterial properties, was published in 1929. The author of the study was Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming.

Fleming's discovery committed actually by accident. On September 3, 1928, he left for the weekend, locking the laboratory. At this time he studied the properties of Staphylococcus aureus. Upon returning, the scientist discovered that due to the general disorder, mold had entered the Petri dish with staphylococcus bacteria. Colonies of bacteria in the places where Penicillium notatum appeared became transparent: the mold destroyed the bacterial cells.
The assistant to whom Fleming told about his discovery recalled that the scientist did almost the same thing in 1922 opened another antibacterial drug is lysozyme. But in that case, mucus from Fleming's nose got into the Petri dish. After the discovery of penicillin, Fleming made a report at the University of London and then wrote an article for a scientific journal. But, despite the importance of the discovery and the ability of penicillin to fight bacterial infections, the discovery did not receive practical development at that time. Work on further study of penicillin was stopped.
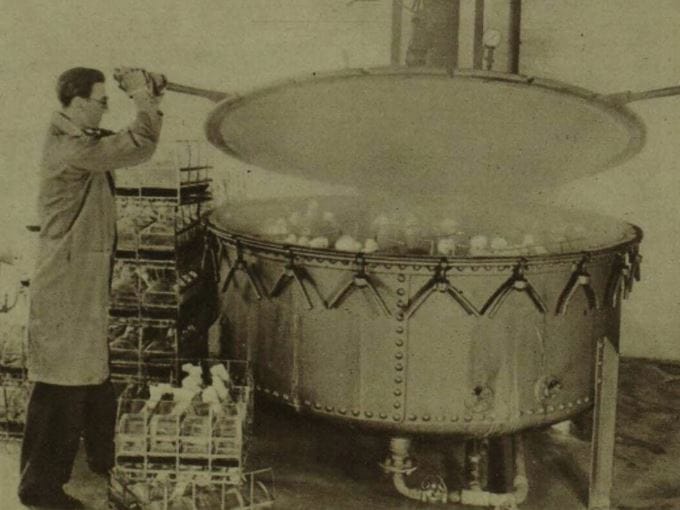
In 1939, a group of Oxford University scientists led by Ernest Boris Chain and Howard Florey resumed research into the properties of penicillin. Cheyne later confessedthat at the beginning of the work his team did not expect to use the substance as a medicine. Over the course of a year, scientists first grew penicillin, trying to figure out how to produce more of the substance. Then in 1940 the drug began to be tested for toxicity. Experimentally, researchers found that penicillin is effective against staphylococcus, streptococcus and gas gangrene. The results of the work were published in the same 1940 in the journal The Lancet.
American researchers from Columbia University drew attention to the article and in 1941 continued the work of their British colleagues, having already conducted experiments on humans. More on this soon wrote newspaper The New York Times, and pharmaceutical companies became interested in penicillin. Since the end of 1942, penicillin has already produced in industrial quantities, having learned to ferment the drug in large containers. By 1944, penicillin was being supplied to the American Army during World War II.

Soviet microbiologist Zinaida Vissarionovna (and not Vasilievna, as the Rostov governor called her) Ermolyeva developed domestic penicillin in parallel with British and American colleagues. In 1942, Ermolyeva, who worked at the All-Union Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology, allocated an analogue of the antibiotic called krustosin. The first clinical trials began in the middle of that year. In 1944, Howard Florey arrived in Moscowto exchange experiences with Zinaida Ermolyeva. British and Soviet scientists compared the resulting drugs to determine their effectiveness. At the end of 1944, the first doses of domestic penicillin began to be sent to the front.
In 1945, the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology was awarded for the discovery of penicillin and its medicinal properties in infectious diseases. The prize was shared between Alexander Fleming (as the discoverer of penicillin), Ernest Boris Chain and Howard Florey (as the scientists who carried Fleming's work to completion). The primacy of Fleming, who discovered penicillin in 1928 and wrote a scientific article about it in 1929, has never been disputed. Zinaida Ermolyeva became famous as the inventor of the first Soviet antibiotic.
Thus, the words of the Rostov governor that penicillin was invented in the USSR before the British do not correspond to reality.
Cover photo: Molecular model of penicillin, London Medical Museum
- Is it true that father and son Flemings saved Winston Churchill from death twice?
- Is it true that Rospotrebnadzor ordered the addition of hormones and antibiotics to drinking water?
If you find a spelling or grammatical error, please let us know by highlighting the error text and clicking Ctrl+Enter.






