Numerous sources claim that the consequences of an ordinary galvanic cell getting into the trash can can be disastrous - a significant area of the earth is poisoned by heavy metals. We checked how accurate the numbers circulated on the Internet are.
This is what it says on the site Russian Geographical Society: “It is believed that one AA battery pollutes about 20 m with lead, mercury and other substances.2 soil, about 400 liters of water. For example, in a forest zone this is the habitat of two trees, two moles, one hedgehog and several thousand earthworms.”
Similar information (accurate to the volume of water) can be read on the websites of such organizations as Bellona Environmental Law Center, Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, Tolyatti State University, Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of the Republic of Tatarstan, Prefecture of the Northern Administrative District of Moscow, in reputable media ("Vedomosti", Interfax), as well as on information stands in many Russian schools. The corresponding announcements usually precede campaigns for separate waste collection and cleanup days. Often information comes with reference to data from the State Biological Museum. K. A. Timiryazeva.
It has long been known that proper disposal of galvanic cells (commonly called batteries) is very important. The reason for this is the heavy metals and toxic chemicals they contain. With all the variety of types of batteries and possibilities for their recycling Rospotrebnadzor highlights the following common key features of these products.
- A battery, even if it has expired, does not pose a danger provided that its casing is not damaged and it is stored at room temperature and minimal humidity. When it ends up in a landfill along with household waste and is exposed to various atmospheric factors, the battery begins to rust and deteriorate due to corrosion. The battery case loses its seal, the contents gain access to the external environment, poisoning it and its inhabitants.
- Alkali and heavy metals from a broken battery pose a danger to the environment. Entering first into the soil, toxic substances reach groundwater, from where they enter water bodies, including those from which tap water is collected. Land and the plants growing on it, including numerous food crops, are exposed to chemical pollution. Meat and milk from farm animals grazing on contaminated pastures also become dangerous. Not only is passive corrosion dangerous, as a result of which batteries pollute the soil and water, landfills often undergo spontaneous combustion, and batteries in the garbage, when heated, release dioxins into the atmosphere, also polluting the air. Dioxins are tens of thousands of times more poisonous than cyanide and are the cause of cancer and diseases of the reproductive system.
We will not dwell on the legislative framework and actual practice regarding the recycling of batteries in countries around the world - here the picture is completely different, and it is not directly related to our case. We are interested in a purely quantitative question.
If you try to find the information in the title in English, you will get the strong impression that she was born in Russia after all - the vast majority links lead to English-language versions of Russian or near-Russian sites. The earliest mention of the fact in Runet dates back to October 25, 2010, when Komsomolskaya Pravda published article under the heading “Save the hedgehogs - bring the batteries to us!” In it, Nizhny Novgorod schoolchildren talked about square meters, trees, moles, hedgehogs and worms (although in the video attached to the article they only mentioned square meters).
As for alternative data, for example, the leading Chinese newspaper People's Daily in 2001 wrote about pollution of 1 m3 soil and 12 m3 water (12,000 l). On the Green Europe 2021 project page were mentioned 4 m2. But on Ukrainian sites the picture is somewhat different: the number in 16 m2 (and on website Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant - 16 m3). And here we can finally get acquainted with the scientific basis. The fact is that in 2018, volunteers of the project “Batteries, Give Up!” together with the national university "Lviv Polytechnic" held study, which consisted of three stages;
1. determination of the composition of the batteries under study;
2. determination of the concentration of chemical elements in the studied samples (by chemical means);
3. calculation of soil pollution with multi-cell batteries.
The objects of study were AA batteries of 25 models and three types (seven lead-free salt batteries, eight alkaline batteries, ten lead-free salt batteries). Here, for example, is the composition of a battery from one well-known brand:
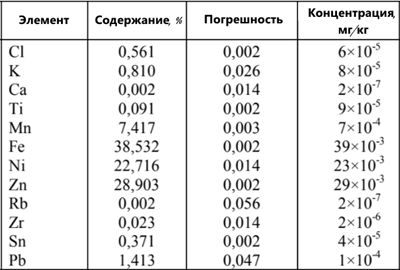
As you can see, this small product contains 12 chemical elements at once, 11 of which are metals.
As a result, through complex mathematical and physical calculations, it was established that one AA battery pollutes approximately 16.75 m2 area, or 134 m3 soil. On the scale of the degree of danger for the ground, this corresponds to the “dangerous” indicator. Since this is the most detailed quantitative analysis available of the environmental impacts of galvanic cells, we can take it as a model and summarize: Russian environmentalists, speaking of 20 m2 contaminated area were quite close to the truth.
Mostly true
Read on the topic:
If you find a spelling or grammatical error, please let us know by highlighting the error text and clicking Ctrl+Enter.







